Ball splines were once a staple for many machine designers seeking an elegant way to integrate rotary and linear motion. Driven by pressures to speed their machines to market, many designers found it faster to implement pre-packaged solutions in which shafts for both rotary and linear motion had already been integrated.
Now, as emerging opportunities for automation bring more axes of motion to machinery, more designers are finding that packaged solutions may not have enough flexibility to meet application requirements. This shift has caused many designers to reconsider ball splines, mostly because of their unique ability to integrate rotary and linear motion on a single shaft. This capability provides advantages for motion performance and stability, giving designers more ways to compress an assembly, extend a stroke or distribute a load, as well as new flexibility to meet modern automation demands.
How ball splines work
Like ball screws, ball splines provide nearly friction-free motion by restricting physical contact to tangential points of rolling balls, which are guided by ball screw threads and the raceways within a nut. Ball splines then augment this rotary guidance by adding one or more linear grooves?-aka splines?-along the shaft, which facilitate front-to-back movements. (Figure 1) These grooves provide a low-friction linear path while simultaneously enabling transmission torsional loads.
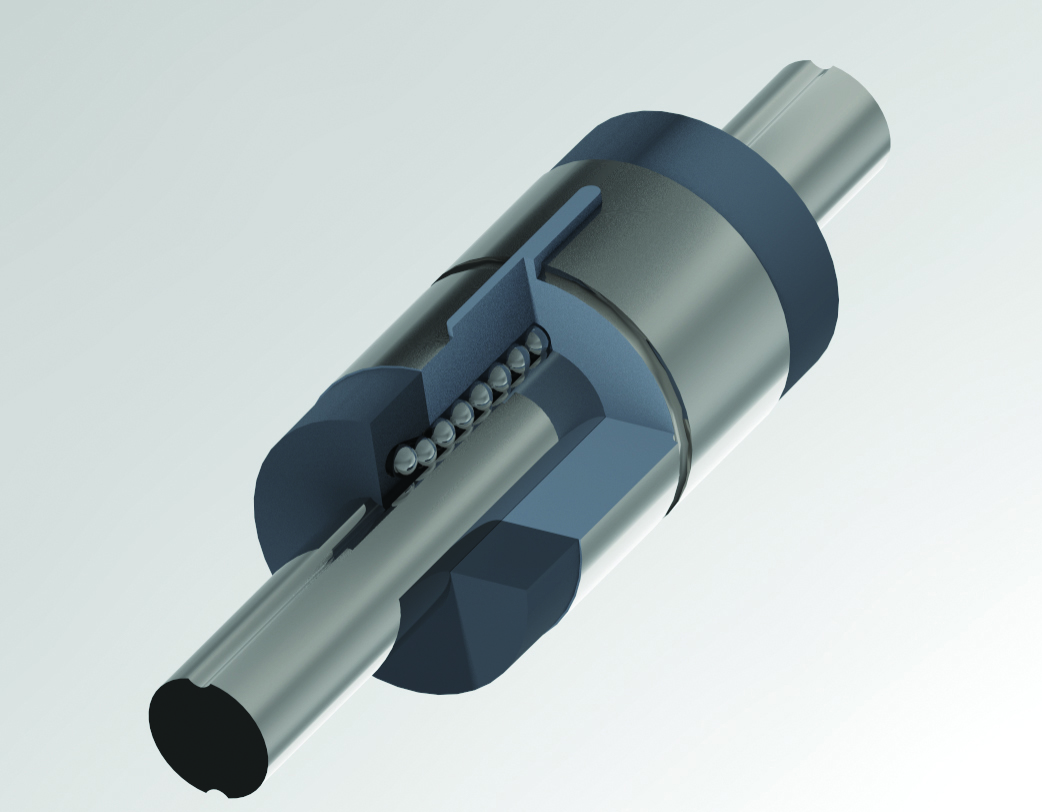
Figure 1. Ball splines have one or more grooves that guide balls to enable nearly friction-free linear or rotary motion. (Image courtesy of Thomson Industries, Inc.)
The result is a highly efficient coupling device suitable for various applications involving axial load transfer or torque transmission. Ball splines resist the radial displacements caused by torque loads and need small forces to achieve axial displacement of the spline member while transmitting torque. This makes them capable of high-speed operation under high torsional loads.
Recapturing space
Integrating linear and rotary motion without using a ball spline typically requires mounting separate shafts in a dual-stacked, four-bearing architecture built around Cartesian coordinates. This setup takes time to build and test, consumes a lot of space, and can require higher maintenance interaction. Ball splines enable a single-shaft solution that provides greater design flexibility and requires much less space.
Stability
In addition to reducing the number of shafts needed, the spline structure itself adds stability. The solidness of a ball spline provides a cost-effective way to extend a vertical stroke beyond the scope of what a robot might provide. It also enables cantilevered architectures and can add anti-rotational guidance.
Enhancing performance
To those compressed, stable assemblies, ball splines bring the characteristic performance advantages of other ball screw components. The reduced friction enables higher-speed operations, less wear, longer, more predictable life expectancy, less backlash and seizure, and no stick-slip.
Twists and turns
Ball splines are especially appropriate for automation applications that, traditionally, humans might perform with the twist of a wrist, such as moving a test tube or opening the lid of a sample jar for a laboratory scale. High-speed pick-and-place applications are another example of ball spline use.
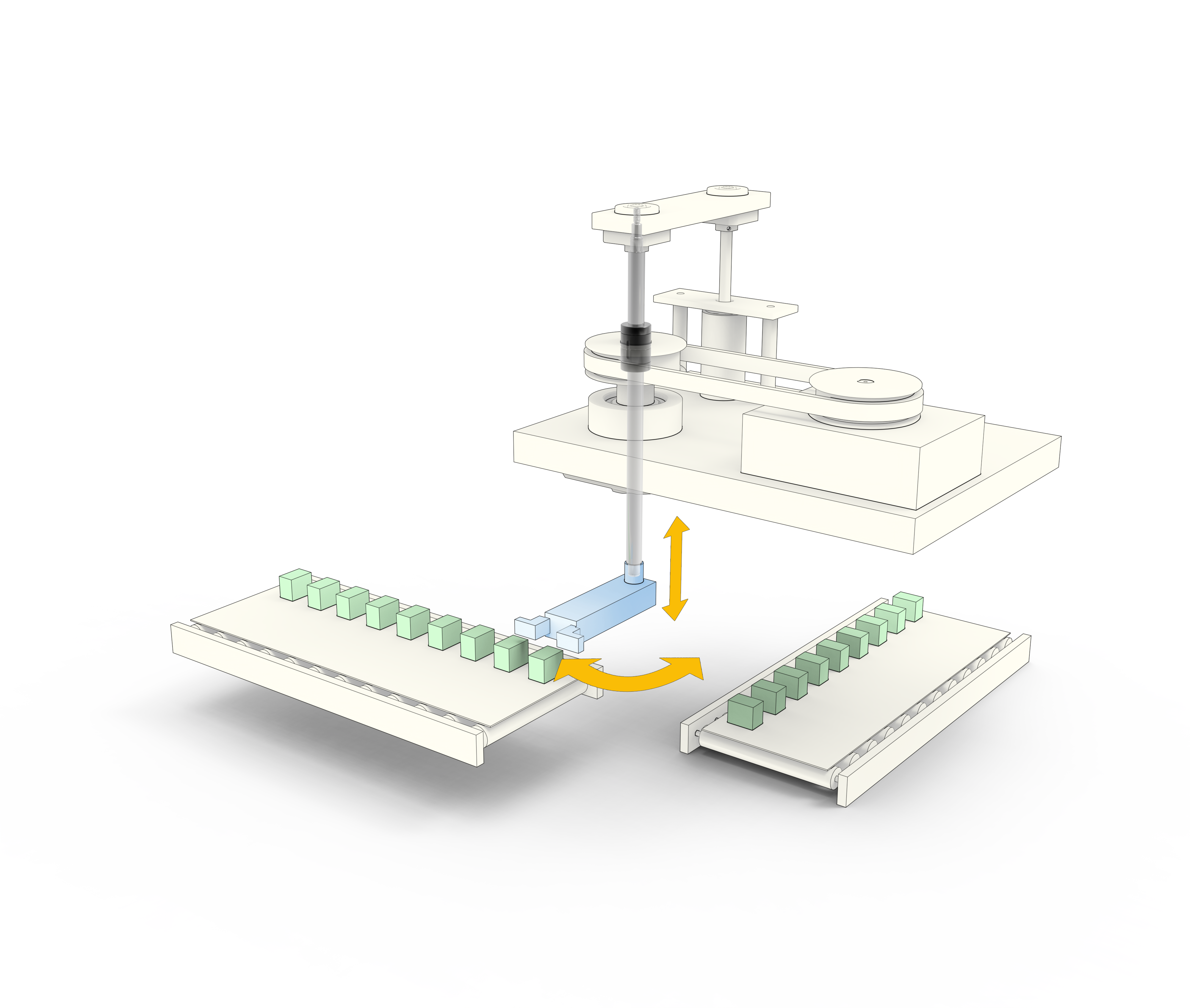
Figure 2. Ball splines can be used in applications that twist and move back and forth, such as pick-and-place machines. (Image courtesy of Thomson Industries, Inc.)
Robots can certainly perform many of the same tasks as ball splines and with greater freedom of movement, but if that freedom is not critical to the application, ball splines can offer numerous other benefits and eliminate the high expense of a robot. Ball splines can provide comparable precision in a smaller footprint and move higher loads faster, with more robust mechanics and often at a lower cost of development.
Specification and customization
Initially, integrating rotary and linear motion was the result of collaboration between mechanical and electrical engineers to build a solution using two or more shafts. Today, there are a wide range of off-the-shelf ball spline options with lengths up to 3000 mm and diameters ranging from 6 to 50 mm.
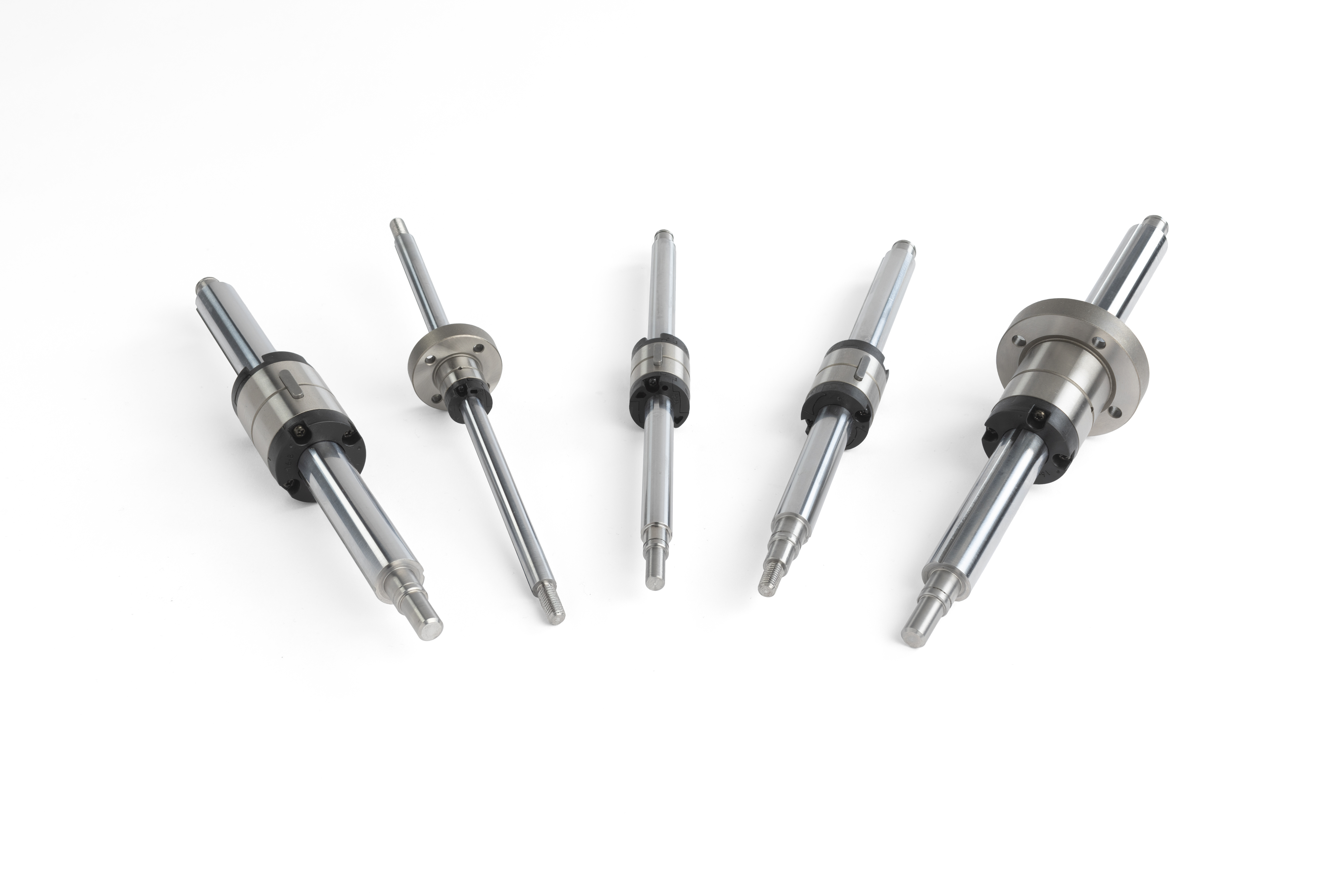

Figure 3. High-precision ball splines are available in a wide range of sizes, nut types and finished ends. Online resources such as the Thomson Ball Spline Selector Tool can help users quickly narrow their options to choose the optimal component for their application. (Image courtesy of Thomson Industries, Inc.)
Ball splines are also quite amenable to customization. Depending on the specification, manufacturers can often tap holes, add reductions for radial bearings or coaxial holes, or make other modifications that may be needed to integrate the ball spline unit into the machine.
Back to the future
When designing a solution, the ability to extend a stroke or compress a system may be the key factor to success. Ball splines provide this game-changing flexibility that designers may not find in a pre-packaged, multi-shaft assembly. More actions that may have previously required a technician or assembler can now be automated, making those movements safer and more efficient, with better control. These types of automated solutions are especially relevant amidst today’s rising labor costs, labor shortages and high absenteeism.
Machine designers should consider ball splines for any application requiring both rotary and linear motion, especially if space is at a premium and if stroke, load, high speed, reliability, or durability are critical.
For those already familiar with ball splines, it may be time to revisit their use in your design. The advances in digital technology make them easier to incorporate into integrated axes of modern systems. For those engineers not familiar with ball splines, it’s a good idea to review your design projects and see if integrating rotary and linear motion on a single shaft could provide space savings, improved cycle time, or better machine reliability.



